Sustainability and Urban Vertical Gardens
Urban vertical gardens are transforming city landscapes, integrating the principles of sustainability with innovative design. These living walls utilize unused vertical spaces, helping mitigate urban heat, purify the air, and promote biodiversity. As cities continue to grow and face environmental challenges, vertical gardens represent a compelling solution that supports ecological balance and enhances the quality of life for urban residents. Through a deeper exploration of their environmental impact, architectural integration, social benefits, and future possibilities, it becomes evident that urban vertical gardens are integral to a more sustainable urban future.
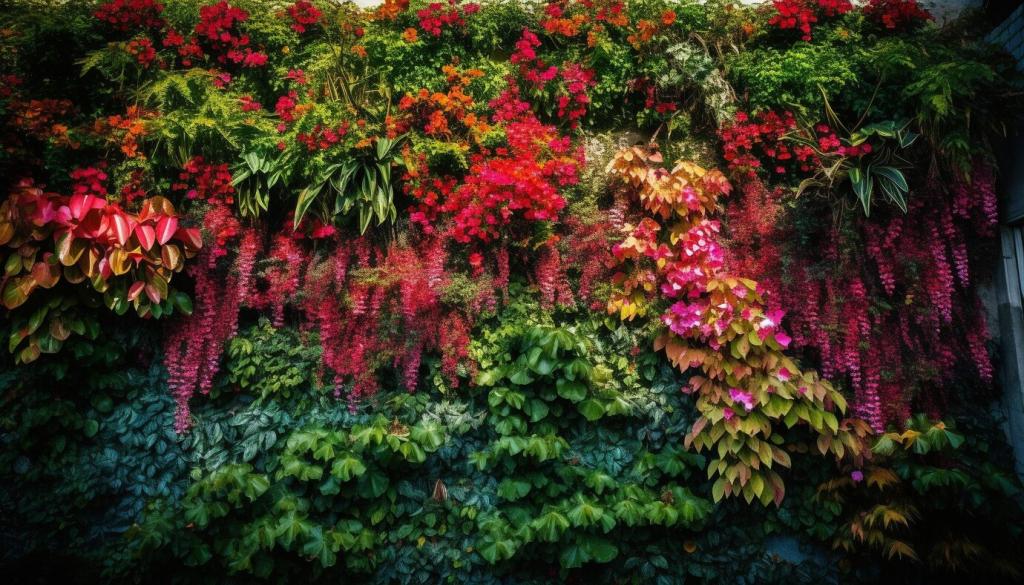


Environmental Impact of Vertical Gardens
Urban environments often struggle with poor air quality due to the concentration of pollutants from vehicles and industrial activity. Vertical gardens play a pivotal role in improving air quality by trapping dust particles and absorbing harmful gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. The leaves and roots of the plants act as natural filters, removing toxins from the air and releasing purified oxygen. Over time, urban areas with a high density of vertical greenery can experience a noticeable improvement in air clarity, which benefits public health and supports a more livable urban climate. Additionally, incorporating a variety of plant species can maximize pollutant absorption and contribute to a richer urban ecosystem.
Integrating Vertical Gardens into Urban Architecture
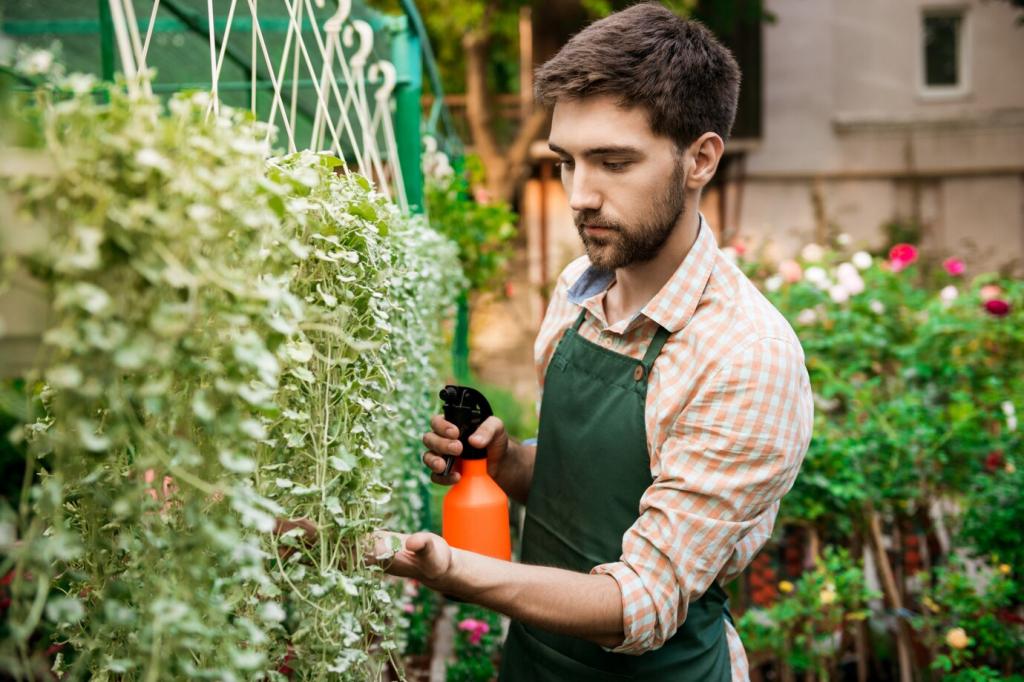
Incorporating vertical gardens into buildings requires careful planning and selection of materials suitable for diverse climates and structural conditions. Lightweight substrate systems and automated irrigation are commonly employed to ensure healthy plant growth with minimal maintenance. The choice of plant species is also crucial, as it influences both the garden’s visual appeal and its ecological benefits. Designers often collaborate with botanists to select resilient, low-maintenance plants that can withstand urban pollution and variable weather. The success of a vertical garden lies in its capacity to blend seamlessly with architectural elements, ensuring longevity and functionality within the urban environment.
Community and Social Benefits

Improving Mental Health and Well-Being
Contact with greenery and natural elements has been consistently linked to improved mental health outcomes. Vertical gardens bring nature directly into dense urban spaces, providing restorative environments amidst concrete and noise. These living walls can reduce stress, enhance mood, and promote relaxation for passersby, office workers, and nearby residents. The visual serenity and engagement with nature encourage mindfulness and a sense of connection to the environment, which are increasingly essential in cities facing rapid population growth and high stress levels. By weaving natural beauty into everyday settings, vertical gardens offer urban citizens an accessible source of calm and inspiration.

Fostering Social Interaction and Engagement
Vertical gardens become focal points for community interaction, drawing together diverse groups of people. Their installations often stimulate neighborhood pride and cooperation as residents participate in planting, maintenance, or educational workshops. Public vertical gardens in parks, schools, and plazas provide platforms for learning about sustainability and gardening, empowering individuals to engage with environmental issues firsthand. These communal activities foster a spirit of collaboration, breaking down social barriers and nurturing a sense of ownership and belonging within the urban landscape. Ultimately, vertical gardens help build stronger, more connected communities that value collective environmental stewardship.

Urban Agriculture and Food Security
Incorporating edible plants into vertical gardens unlocks new opportunities for urban agriculture. These productive green walls can yield herbs, vegetables, and fruits, offering a local source of fresh produce in areas with limited ground-level gardening space. Community organizations, restaurants, and schools are increasingly utilizing vertical gardens to grow food, reduce supply chain dependence, and promote healthy eating habits. By shortening the distance between food production and consumption, urban vertical gardens support food security, reduce transportation emissions, and build resilience against supply disruptions—a vital consideration in today’s rapidly changing world.